City Builder
In this tutorial we'll create a dense grid of buildings, then cut away from them to place roads with curves. We'll also make use of a generator to combine the buildings with the roads.
Setting Up
Create a Bezier Curve object. You can enter edit mode and delete the default curve it creates.
Then create a new script. Setting up an external editor is recommended.
Import Geometry Script, and create a basic tree builder function. We'll add a few arguments to configure the buildings.
from geometry_script import *
@tree("City Builder")
def city_builder(
geometry: Geometry,
seed: Int,
road_width: Float = 0.25,
size_x: Float = 5, size_y: Float = 5, density: Float = 10,
building_size_min: Vector = (0.1, 0.1, 0.2),
building_size_max: Vector = (0.3, 0.3, 1),
):
return geometry
Run the script to create the tree, then add a Geometry Nodes modifier to your curve object and select the City Builder node group.
Buildings
Let's start with the buildings. We'll distribute points on a grid with size_x and size_y.
def city_builder(...):
building_points = grid(size_x=size_x, size_y=size_y).distribute_points_on_faces(density=density, seed=seed).points
return building_points
Next, we'll instance cubes on these points to serve as our buildings. We move the cube object up half its height so the buildings sit flat on the grid, and scale them randomly between the min and max sizes.
def city_builder(...):
...
return building_points.instance_on_points(
instance=cube().transform(translation=(0, 0, 0.5)),
scale=random_value(data_type=RandomValue.DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, min=building_size_min, max=building_size_max, seed=seed),
)
Roads
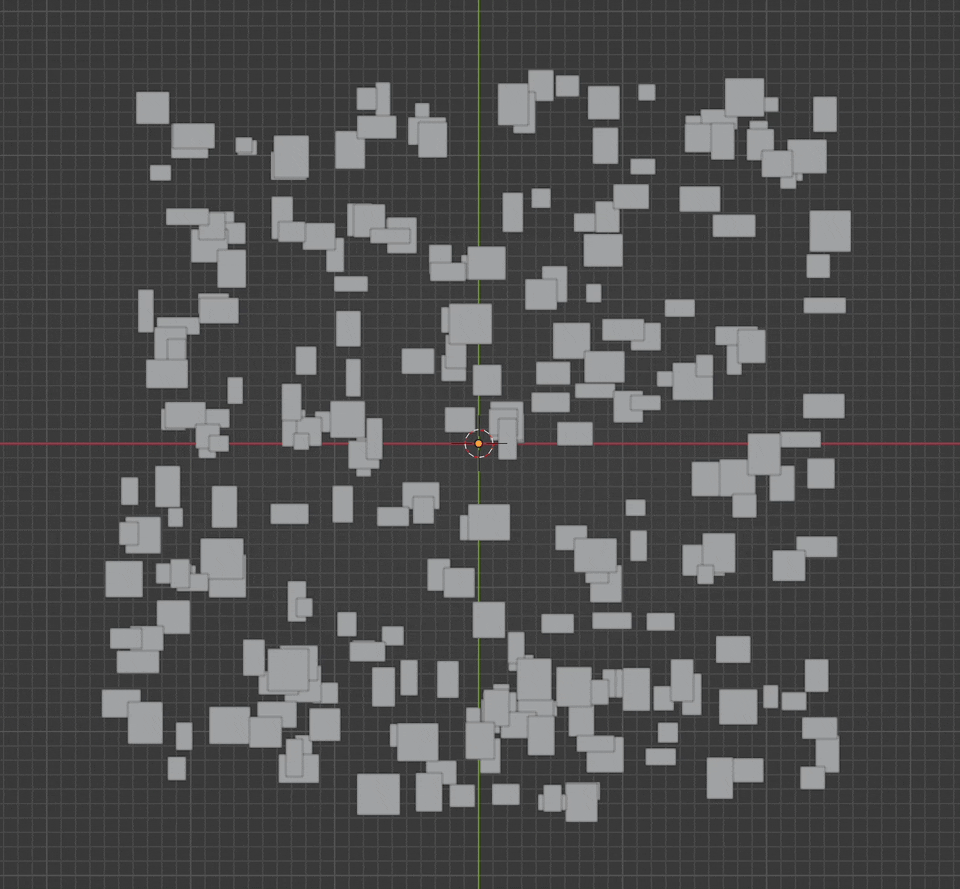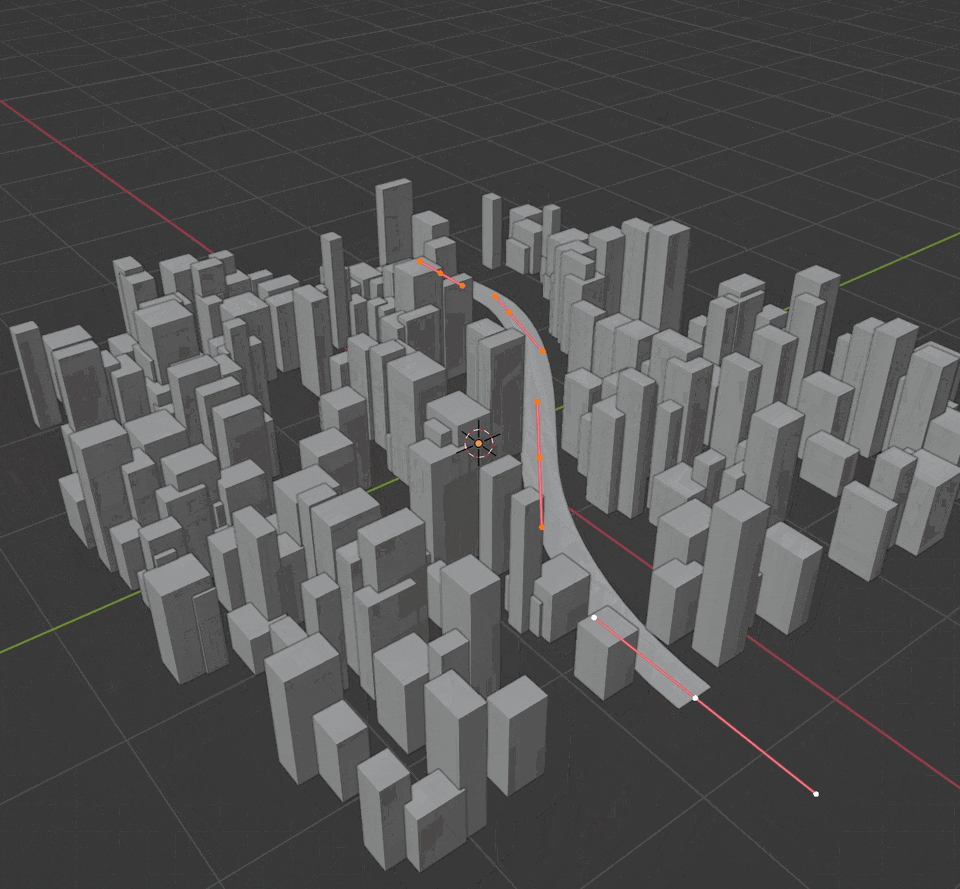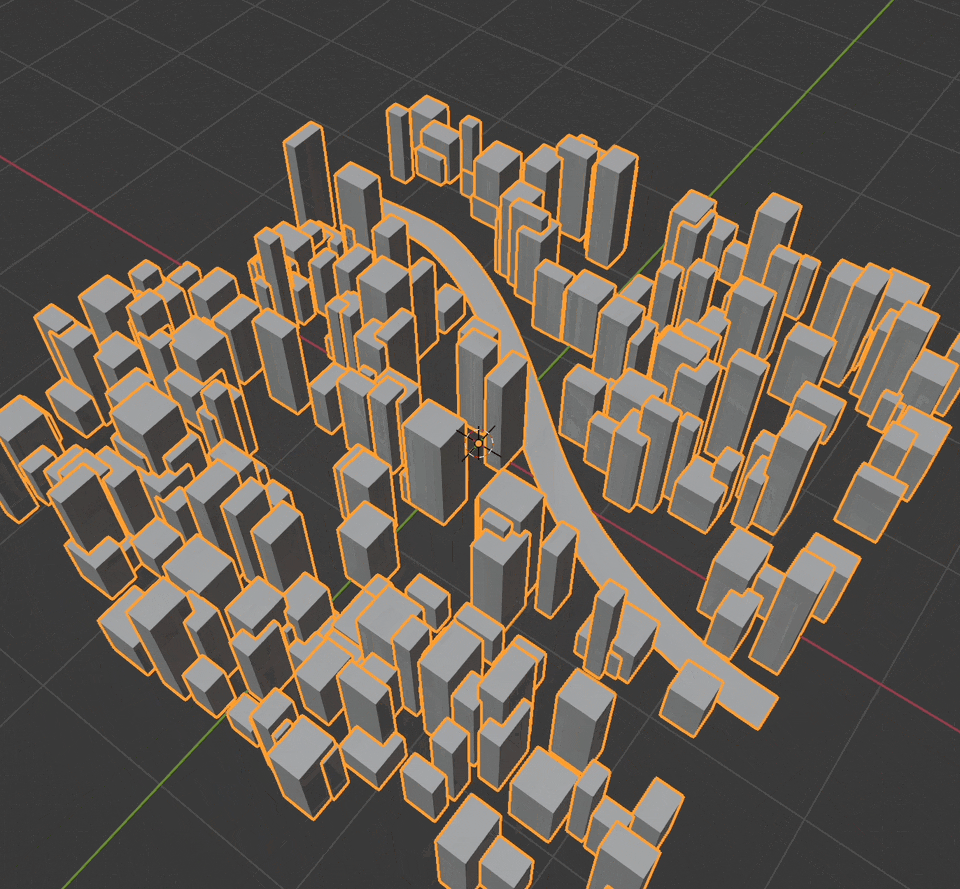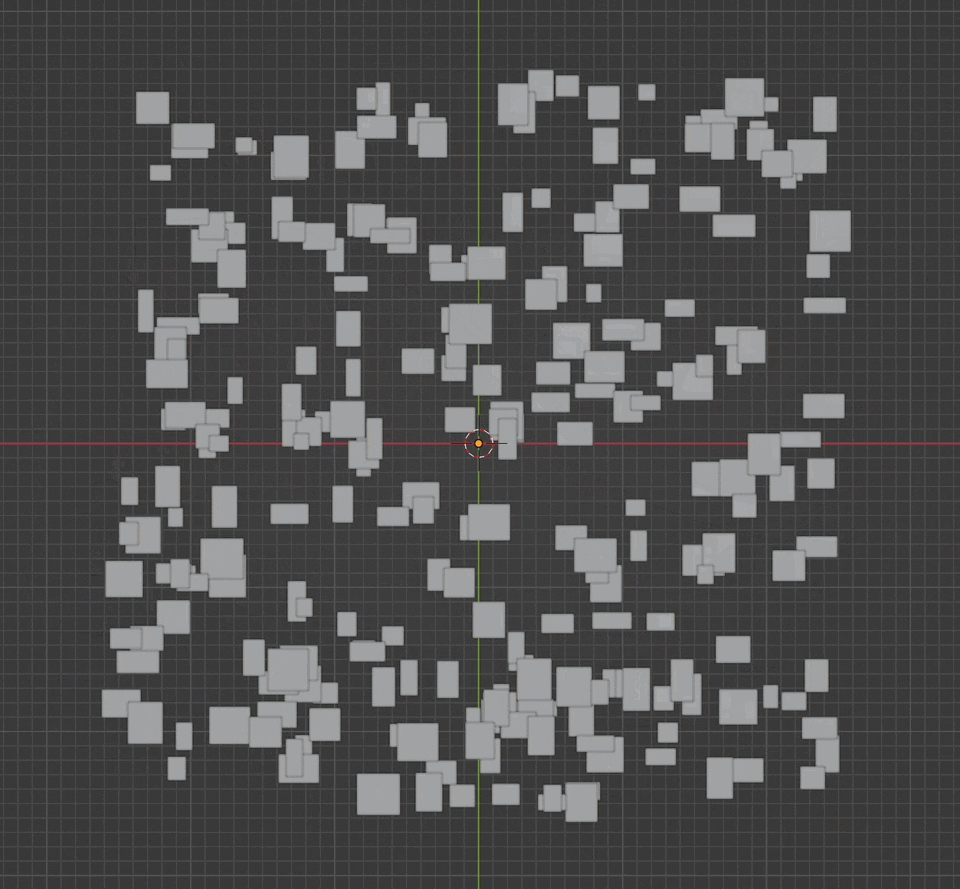
Using curve_to_mesh, we can turn the input curve into a flat mesh. We'll use the yield keyword to join the curve mesh and the building mesh automatically. Change the building_points.instance_on_points line to use yield for this to work.
def city_builder(...):
yield geometry.curve_to_mesh(profile_curve=curve_line(
start=combine_xyz(x=road_width * -0.5),
end=combine_xyz(x=road_width * 0.5)
))
...
yield building_points.instance_on_points(...)
But now the buildings are overlapping the road. We need to remove any point that falls within the road curve. We'll use geometry_proximity and delete_geometry to find and remove these invalid points.
def city_builder(...):
...
building_points = ...
road_points = geometry.curve_to_points(mode=CurveToPoints.Mode.EVALUATED).points
building_points = building_points.delete_geometry(
domain=DeleteGeometry.Domain.POINT,
selection=geometry_proximity(target_element=GeometryProximity.TargetElement.POINTS, target=road_points, source_position=position()).distance < road_width
)
...
Drawing Roads
Enter edit mode and select the Draw tool. Simply draw roads onto your city to see the buildings and meshes update.

Final Script
from geometry_script import *
@tree("City Builder")
def city_builder(
geometry: Geometry,
seed: Int,
road_width: Float = 0.25,
size_x: Float = 5, size_y: Float = 5, density: Float = 10,
building_size_min: Vector = (0.1, 0.1, 0.2),
building_size_max: Vector = (0.3, 0.3, 1),
):
# Road mesh
yield geometry.curve_to_mesh(profile_curve=curve_line(
start=combine_xyz(x=road_width * -0.5),
end=combine_xyz(x=road_width * 0.5)
))
# Building points
building_points = grid(size_x=size_x, size_y=size_y).distribute_points_on_faces(density=density, seed=seed).points
road_points = geometry.curve_to_points(mode=CurveToPoints.Mode.EVALUATED).points
# Delete points within the curve
building_points = building_points.delete_geometry(
domain=DeleteGeometry.Domain.POINT,
selection=geometry_proximity(target_element=GeometryProximity.TargetElement.POINTS, target=road_points, source_position=position()).distance < road_width
)
# Building instances
yield building_points.instance_on_points(
instance=cube().transform(translation=(0, 0, 0.5)),
scale=random_value(data_type=RandomValue.DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, min=building_size_min, max=building_size_max, seed=seed),
)
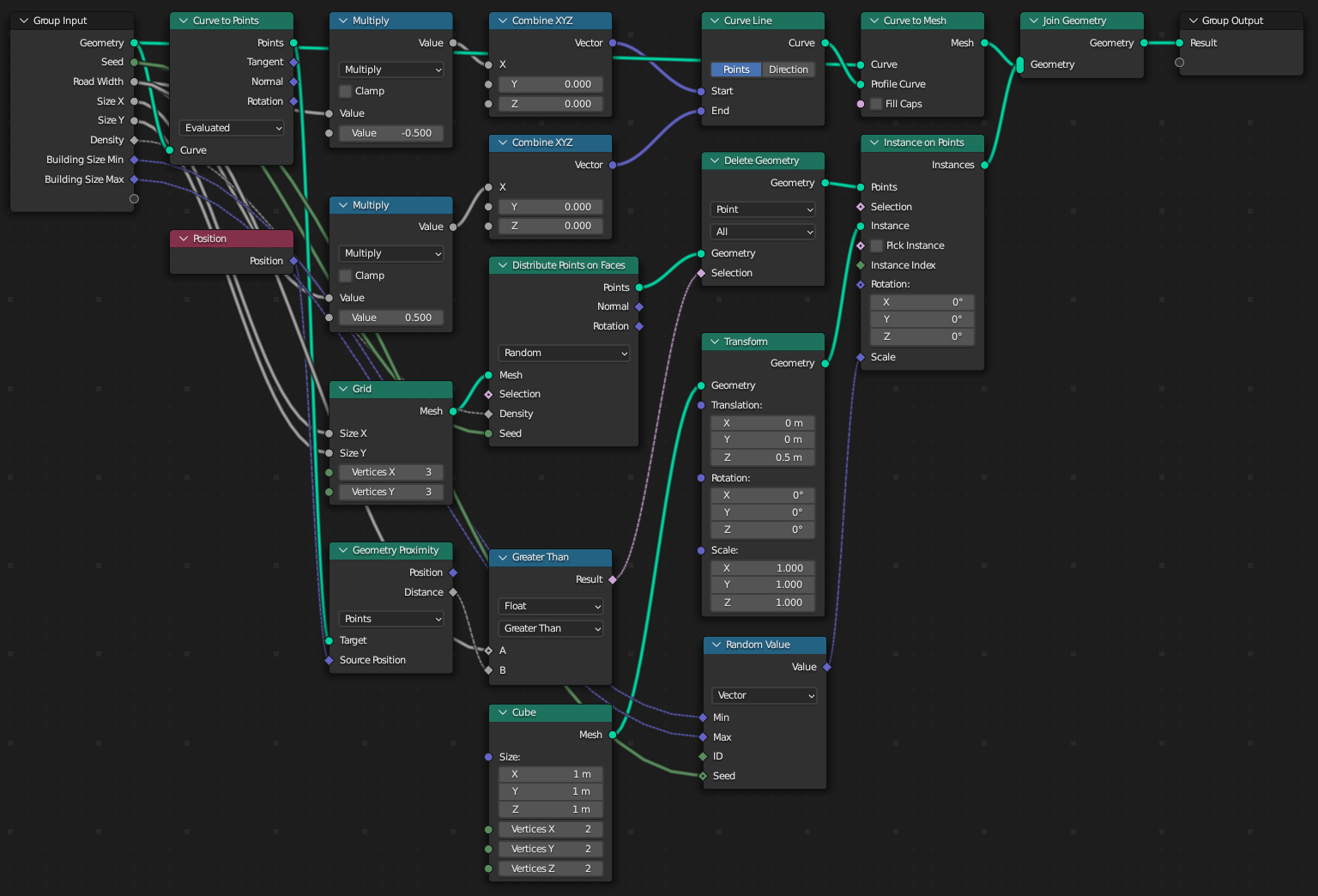
Generated Node Tree