Voxelize
This tutorial walks you through creating a script that turns any mesh into voxels.
This tutorial requires Blender 3.4+ for the Distribute Points In Volume node.
Setting Up
Create a base mesh. I'll be using a Monkey primitive.
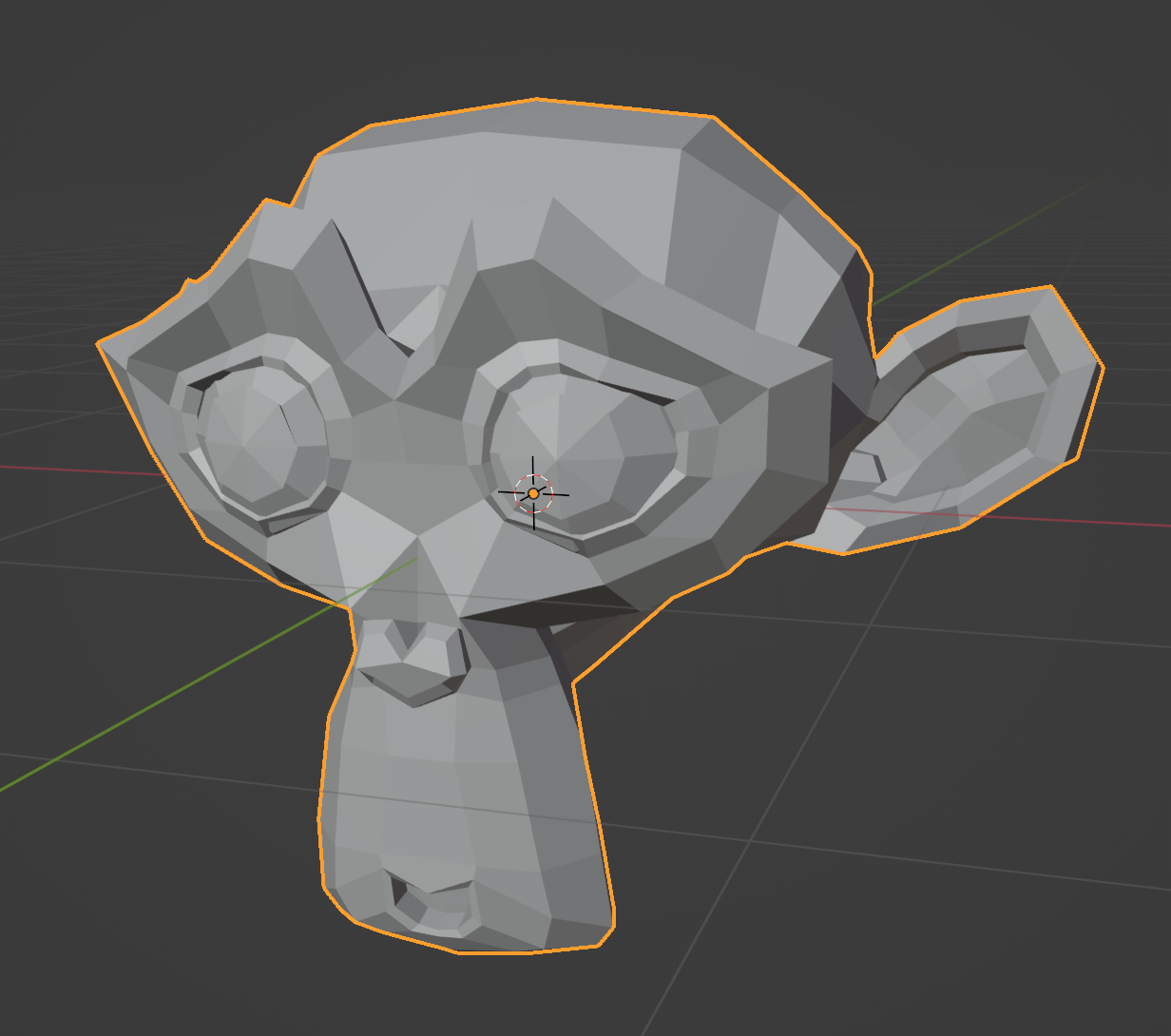
Next, create a new script. Setting up an external editor is recommended.
Import Geometry Script, and create a basic tree builder function. We'll add a geometry argument and annotate it with the Geometry type to receive our base mesh (in this case, a monkey).
from geometry_script import *
@tree("Voxelize")
def voxelize(geometry: Geometry):
return geometry
Run the script to create the tree, then add a Geometry Nodes modifier to your mesh and select the Voxelize node group.
Arguments
Add a new argument resolution: Float. Give it a default value of 0.2. This value will be used throughout the script to configure spacing and voxel density.
def voxelize(geometry: Geometry, resolution: Float = 0.2):
...
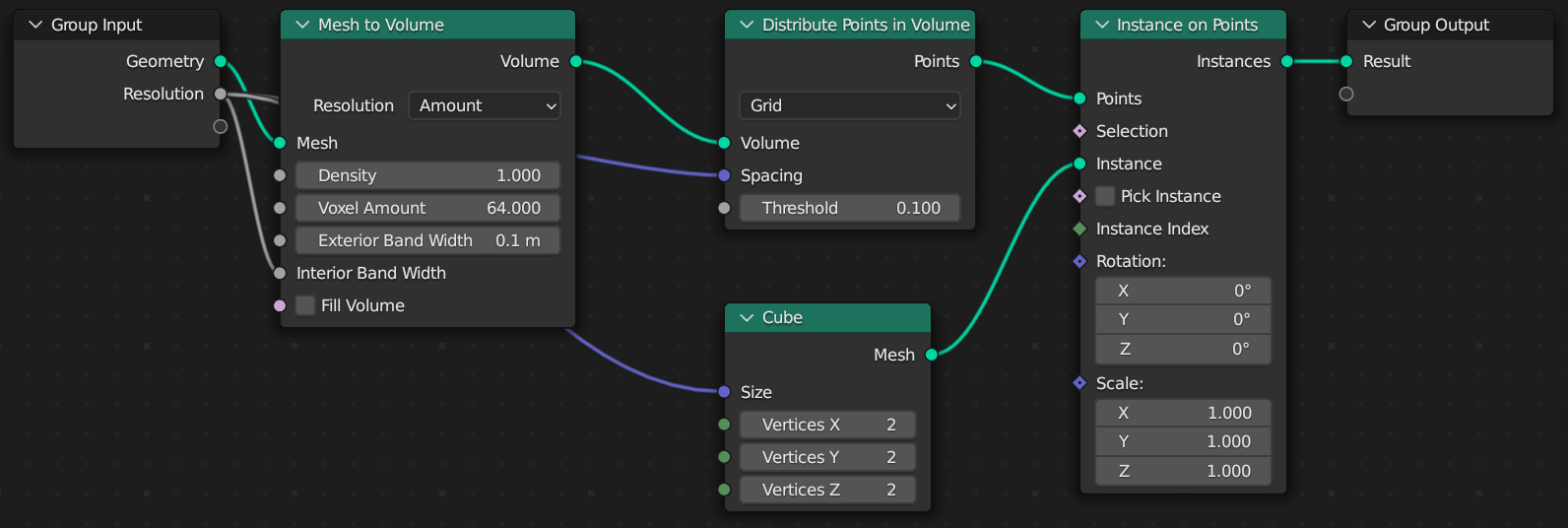
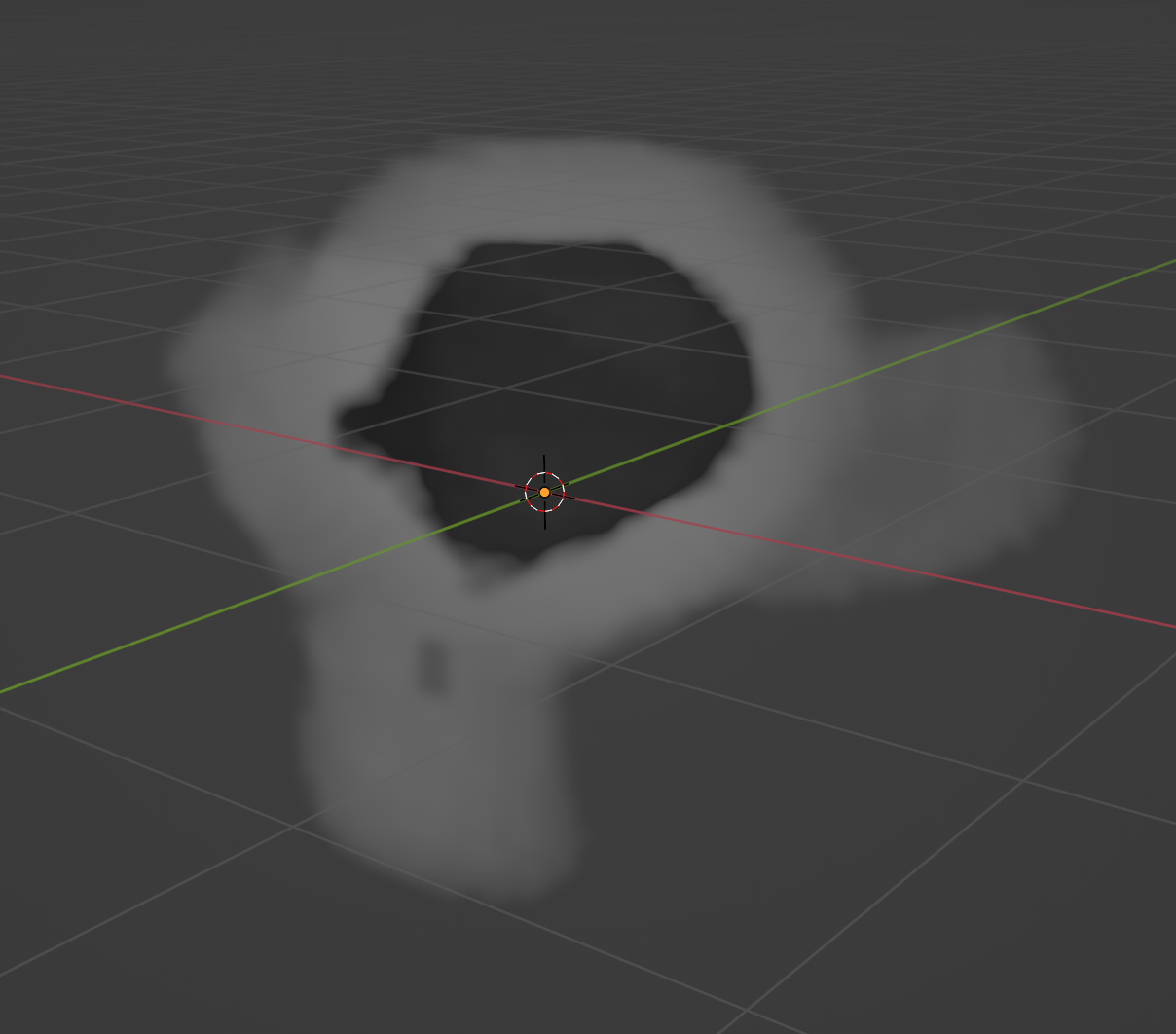
Mesh to Volume
We want to convert the mesh to a hollow volume, so only the outside of the mesh has voxel instances. This will improve the performance of our script.
Use the mesh_to_volume function on the base mesh to convert it to a volume.
def voxelize(geometry: Geometry, resolution: Float = 0.2):
return geometry.mesh_to_volume( # Hollow mesh volume
interior_band_width=resolution,
fill_volume=False
)
Volume to Points
Next, we need to create points to instance each voxel cube on. Use distribute_points_in_volume with the mode set to DENSITY_GRID to create a uniform distribution of points.
def voxelize(geometry: Geometry, resolution: Float = 0.2):
return geometry.mesh_to_volume(
interior_band_width=resolution,
fill_volume=False
).distribute_points_in_volume( # Uniform grid distribution
mode=DistributePointsInVolume.Mode.DENSITY_GRID,
spacing=resolution
)
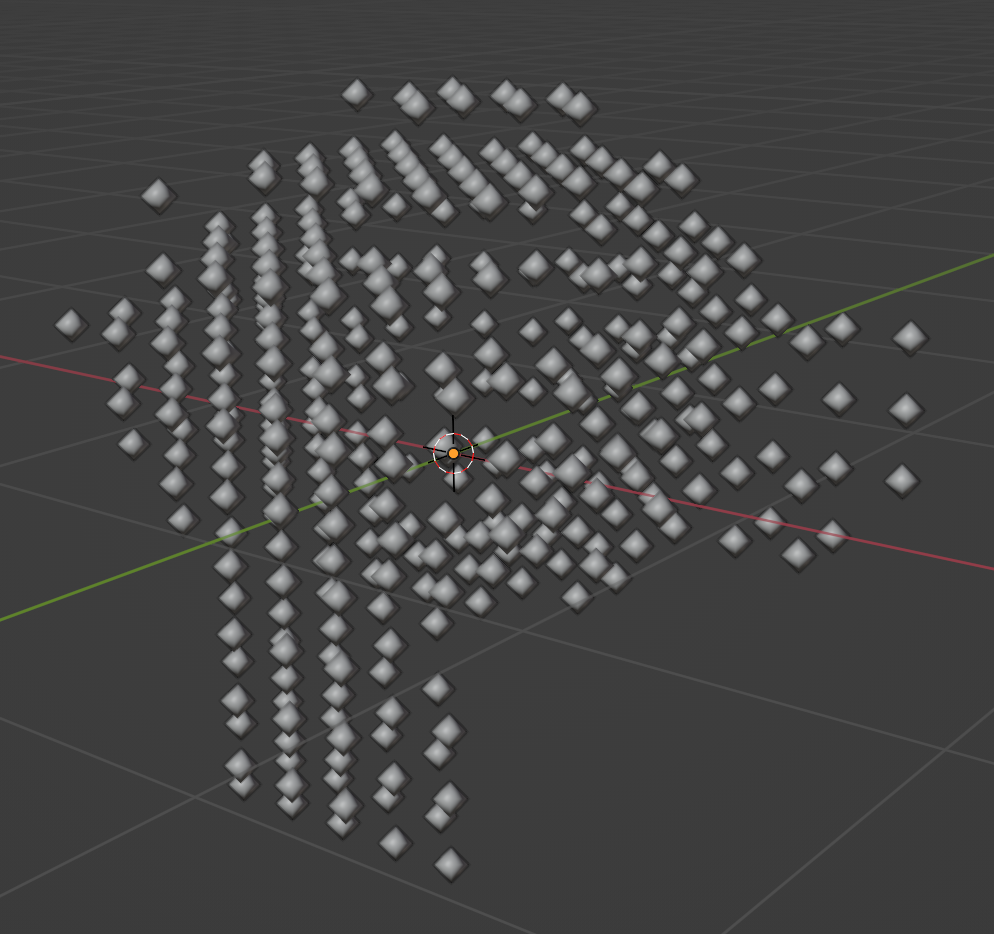
Instance Cubes
Finally, use instance_on_points with a cube of size resolution to instance a cube on each point created from our mesh.
def voxelize(geometry: Geometry, resolution: Float = 0.2):
return geometry.mesh_to_volume(
interior_band_width=resolution,
fill_volume=False
).distribute_points_in_volume(
mode=DistributePointsInVolume.Mode.DENSITY_GRID,
spacing=resolution
).instance_on_points( # Cube instancing
instance=cube(size=resolution)
)
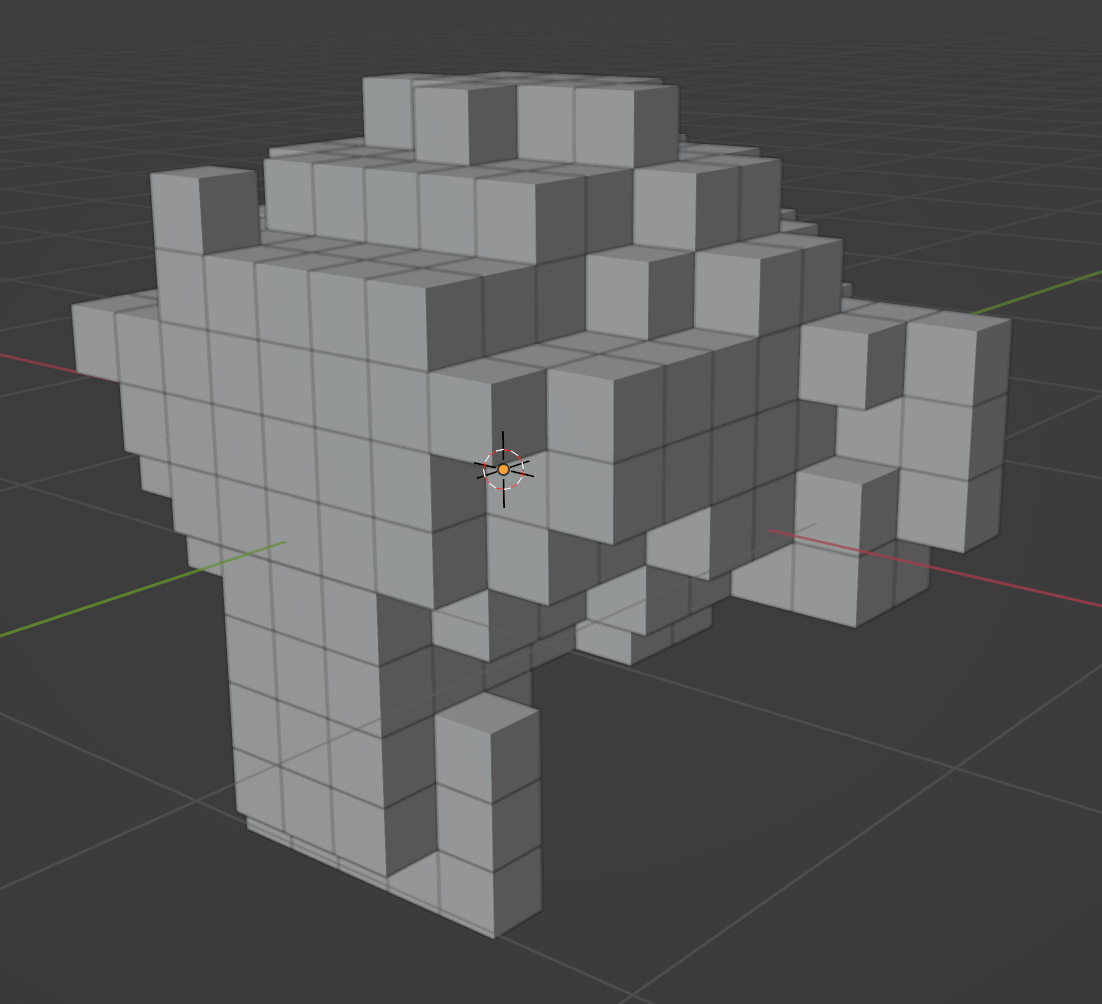
You can lower the resolution to get smaller, more detailed voxels, or raise it to get larger voxels.
Final Script
# NOTE: This example requires Blender 3.4+
from geometry_script import *
@tree("Voxelize")
def voxelize(geometry: Geometry, resolution: Float = 0.2):
return geometry.mesh_to_volume(
interior_band_width=resolution,
fill_volume=False
).distribute_points_in_volume(
mode=DistributePointsInVolume.Mode.DENSITY_GRID,
spacing=resolution
).instance_on_points(
instance=cube(size=resolution)
)
Generated Node Tree